

The effect of chromium(III) concentration on the absorbance of the TEAC-Cr(III) has been examined at wavelength of 488 nm at pH 10-11 with the TEAC solution as blank. Effect of Metal Ion Concentration on Absorption Spectrum and Composition of Complexes Additionally, composition of TEAC-Cr and TEAC-Pb was confirmed by ESI-MS.ģ.2.2. The effect of parameters on the TEAC-Cr and TEAC-Pb complexes formation was also reported.
In this paper, the application of the simultaneous method (H-Point Standard Addition Method, HPSAM) for analysis of Pb(II) and Cr(III) ions using the azocalixarene (TEAC) has been reported.
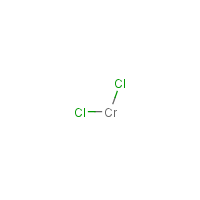
Previously, we have reported simple, fast, sensitive, and spectrophotometric determinations of several metal ions without preconcentration using 5,11,17,23-tetracalix arene (TEAC). Additionally, the high cost is also a problem with many laboratories. Determinations of chromium and lead ions were carried out by many different methods, such as atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). They caused nervous system depressants, cancer risk, and a number of symptoms related to the gastrointestinal tract. Lead and chromium are toxic elements for humans and animals. Moreover, complexations of azocalixarene with metal ions such as Ni 2+, Cr 3+, Fe 3+, Co 2+, Pb 2+, Cu 2+, Hg 2+, and Th 4+ have been studied. The calixarenes had shown applications of optical spectroscopic methods in calixarene chemistry including vibrational spectroscopy, UV-Vis spectrometry, luminescence spectroscopy, ellipsometry, and various optical microscopic methods. Therefore, many reports for metal ions were intensively investigated in recent years. These compounds have recently attracted great interest in a number of fields such as metal extraction, food technology, and environmental engineering. These compounds consist of at least a conjugated chromophore azo (–N=N–) group and two or more aromatic ring groups, which are important classes of organic colorants under different names such as diazotizated calixarene derivatives, “azocalixarenes”. Azocalixarenes are generated by the electrophilic substitution reaction of nitrogen atoms at the p-position unit of the calixarene structure, having several isomers based on the position of the nitrogen atoms and the ring size. A variety of compounds based upon calixarene having nitrophenylazophenol, nitrophenol, indoaniline, indophenol, and azophenol functional groups have successfully designed and exhibited a pronounced chromogenic behavior towards Na +, K +, Cs +, Ca 2+, UO 2 2+, and even chiral amines. Calixarenes are ideal frameworks for the development of chromogenic ionophores in the molecular recognition of ionic species of chemical and biological interests since the incorporation of a suitable sensory group into the calixarene results in a tailored chromogenic receptor. Based on these frameworks, scientists have developed a wide range of derivatives by the alkylation of phenolic groups at the lower rim or modification of upper rim to form many derivatives. The results for several analyzed samples were found to be in satisfied agreement with those acquired by using the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) technique.Ĭalixarenes are a product formed from the condensation reaction of p-substituted phenols with formaldehyde. The proposed method was successfully utilized to invest lead and chromium contents in plating wastewater samples. The H-Point Standard Addition Method (HPSAM) has been applied for simultaneous determination of complexes formation of Cr(III)/Pb(II) and TEAC with concentration from 2 : 1 to 1 : 20 (w/w). Additionally, the molar extinction coefficients were 5 × 10 4 and 1.42 × 10 4 for TEAC-Pb(II) and TEAC-Cr(III), respectively. The complex formation constants (based on Benesi-Hildebrand method) for TEAC-Pb(II) and TEAC-Cr(III) were 4.03 × 10 4 and 1.2 × 10 4, respectively. The ratio of TEAC and metal ion in complexes was found to be 1 : 1 under investigated condition. New complexes of 5,11,17,23-tetracalixarene (TEAC) with Pb(II) and Cr(III) were prepared in basic solution with a mixture of MeOH and H 2O as solvent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
